By Dr. Nathan Orvets, ROC Orthopedics
If your shoulder is in pain, you likely want to know the cause and how to find relief. Shoulder pain can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from injuries to underlying conditions. In this post, we’ll explore the common causes, symptoms, and various treatment options to help you manage and alleviate your shoulder pain.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can stem from various factors, each presenting unique symptoms and requiring different treatment approaches. The shoulder joint is a complex structure, consisting of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to provide a wide range of motion. However, this complexity also makes it susceptible to injuries.
While many shoulder conditions can lead to pain, three of the most common causes of shoulder pain are rotator cuff tears, bursitis, and arthritis. In the following sections, we’ll examine these three conditions more closely.
Rotator Cuff Tears
The rotator cuff consists of a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and allow for a wide range of movements. Rotator cuff tears can be caused by various factors, including age related degenerative changes, inflammation, injury, or changes in the bone around the rotator cuff. This condition often leads to severe shoulder pain and weakness, making it difficult to lift your arm or perform daily tasks.
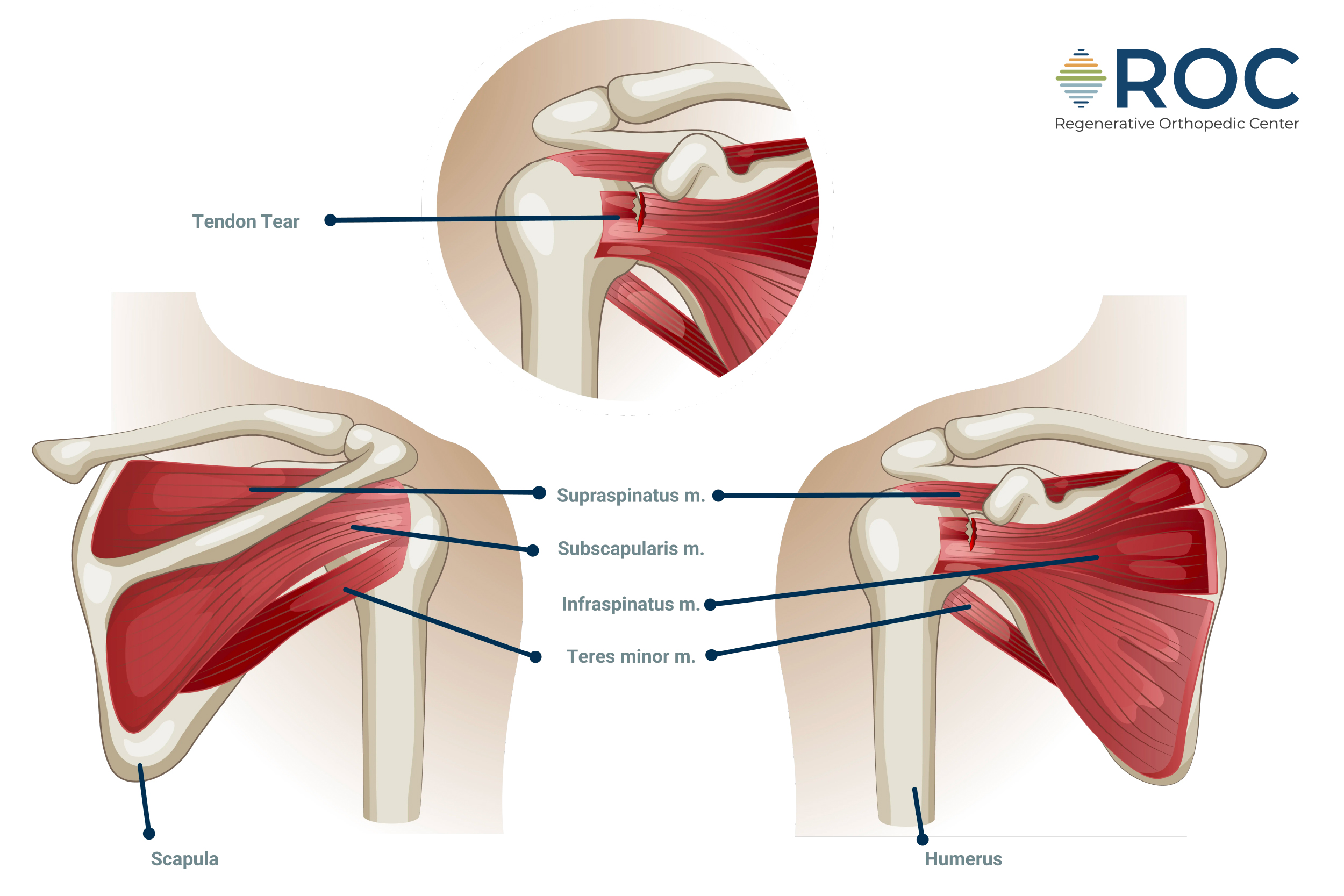
Nonsurgical treatments for rotator cuff tears include rest, ice, pain relief medications, and physical therapy. Surgery may be necessary for severe tears that do not respond to conservative treatments to repair the damaged muscles and tendons.
Bursitis
Bursitis occurs when fluid-filled sacs, or bursae, that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints become inflamed. This inflammation often results from overuse or injury, such as a fall. The condition can cause pain and swelling, making it difficult to move the shoulder.
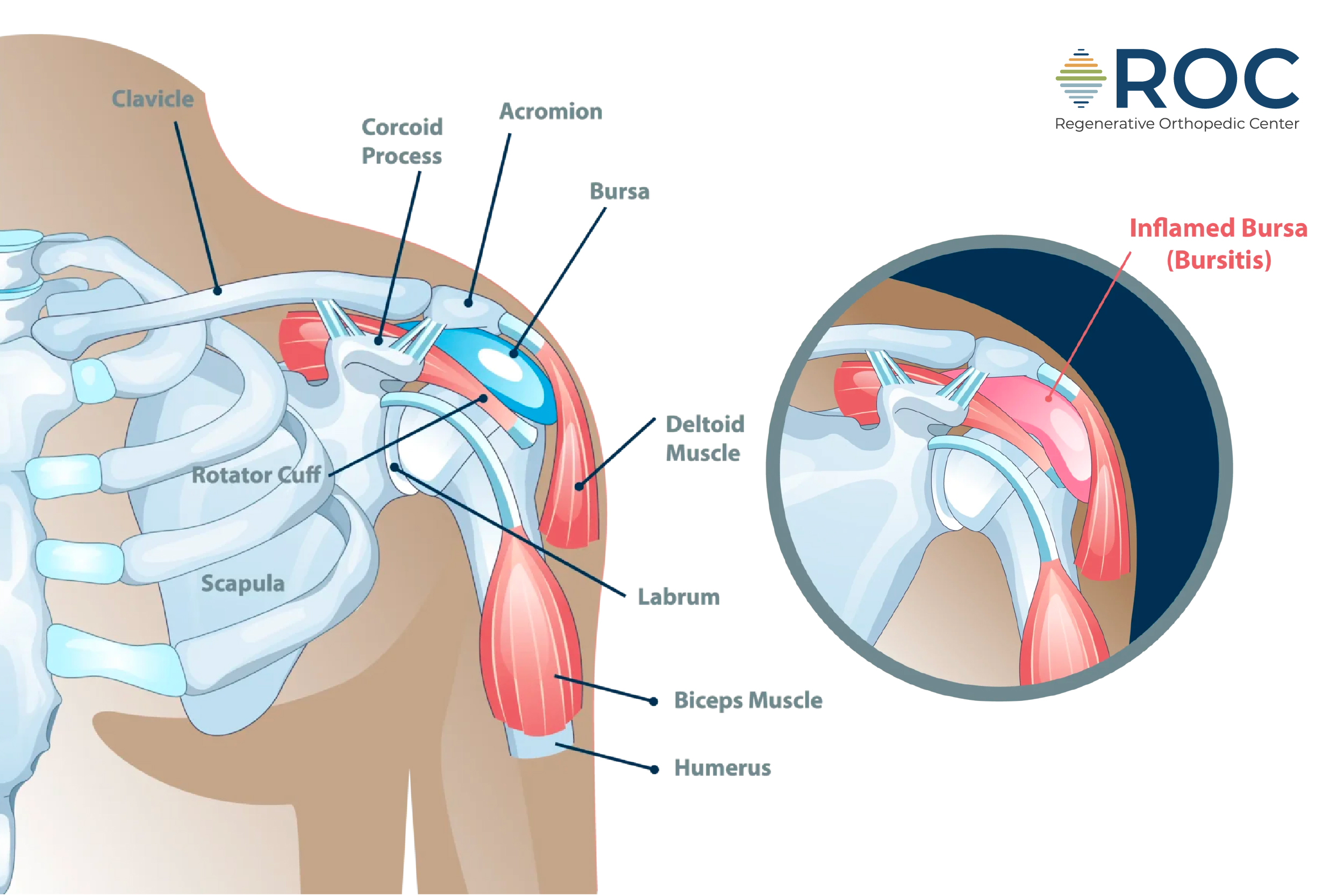
Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve shoulder mobility and strength, helping to prevent future episodes of bursitis.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a common cause of shoulder pain, particularly in older adults. Osteoarthritis, the most common type, results from the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the shoulder joint, leading to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, causes inflammation in the joint lining, which can also affect the shoulders.
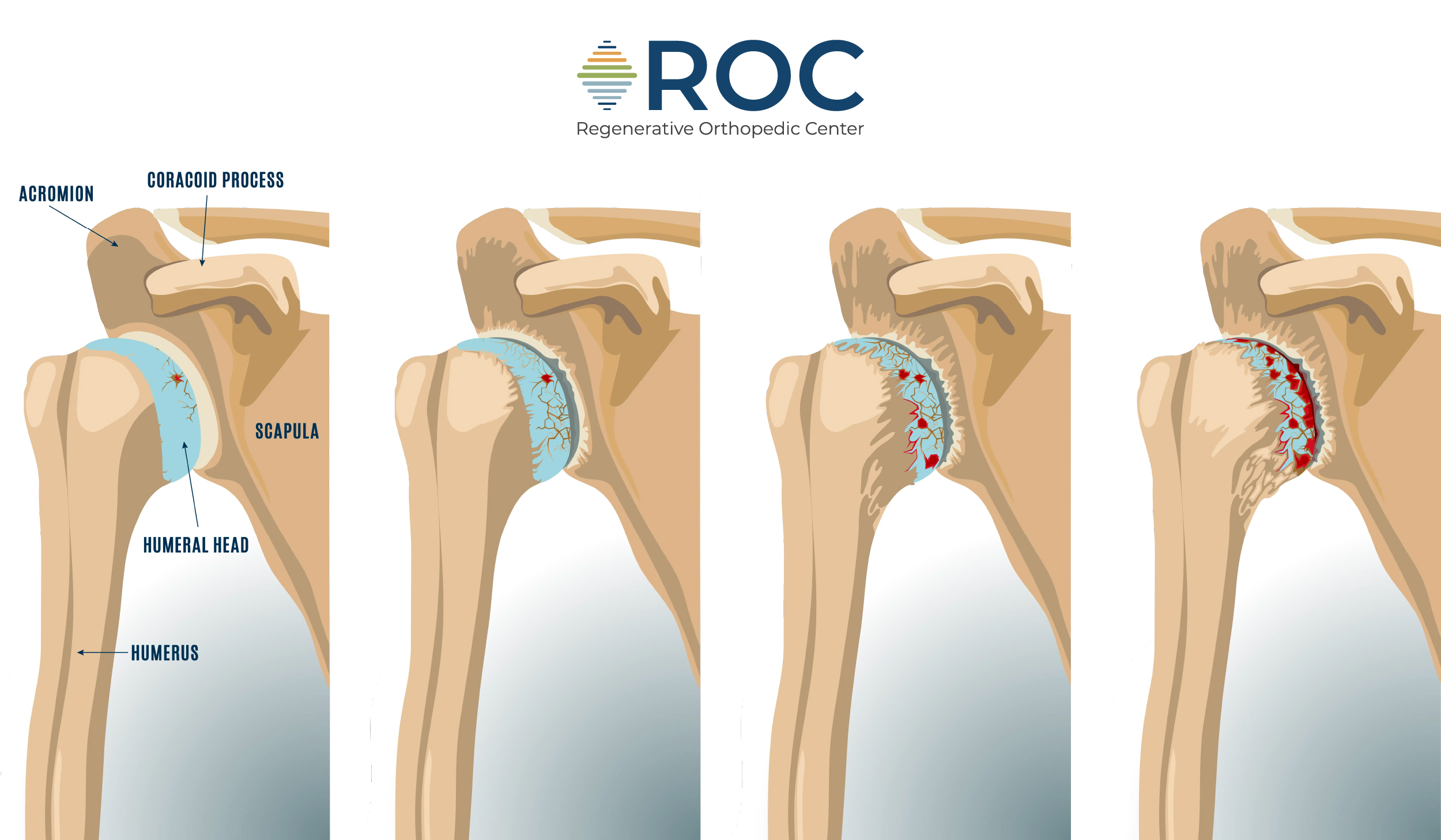
Symptoms may include persistent shoulder pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Treatment options for arthritis in the shoulder include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation, physical therapy to improve joint function, and, in more severe cases, surgery. Maintaining an active lifestyle and performing regular exercises can also help manage symptoms and improve shoulder health.
Recognizing Symptoms of Shoulder Pain
Identifying the symptoms of shoulder pain helps in seeking timely and appropriate treatment. Shoulder pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, intense pain and may radiate to other areas like the neck or down the arm.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the difference between sudden shoulder pain and chronic pain.
- Sudden Shoulder Pain: Shoulder pain can occur suddenly, sometimes with a clear cause, and other times without any obvious trigger. It may be accompanied by other symptoms, including swelling, bruising, visible joint deformation, and tenderness. It can result from an underlying condition or from an injury such as a shoulder dislocation. If sudden pain is severe or does not improve, consider seeking medical evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and ensure a quicker recovery.
- Chronic Pain: Chronic shoulder pain involves persistent discomfort that may worsen gradually over time. Conditions like arthritis or repetitive stress injuries are common culprits. Chronic shoulder pain can impact daily activities, making it difficult to perform tasks that involve lifting, reaching, or even simple movements. Consider consulting a healthcare professional if shoulder pain persists despite rest, worsens, or affects daily activities. An experienced shoulder specialist can identify the underlying cause and suggest appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Shoulder Pain
Accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment. A combination of physical examinations and imaging tests can often discern the root cause of the pain and guide an appropriate treatment plan.
- Physical Examination: In a physical examination, your doctor will assess the shoulder for abnormalities, tenderness, strength, and range of motion, evaluating specific movements to identify the source of pain. This process helps to pinpoint the location and nature of the problem.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests like X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide detailed visualizations of the shoulder, helping identify issues such as rotator cuff tears, bone spurs, or other abnormalities. MRIs are particularly valuable for visualizing soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This comprehensive approach helps ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Effective Treatments for Shoulder Pain
Treatment options for shoulder pain vary from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to surgical intervention, depending on the underlying cause. The aim is to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent future injuries.
Nonsurgical Options
Rest and medication are often the initial treatment approaches for managing shoulder pain. Avoiding or modifying movements that worsen the pain is an important part of treatment. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Corticosteroid injections may be recommended for short-term pain relief.
Physical therapy is often recommended and can play an important role in recovery. Therapeutic exercises tailored to the specific shoulder condition can enhance recovery and improve functionality by strengthening muscles, improving range of motion, and reducing pain. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to address the specific needs of the patient, helping relieve shoulder pain and prevent future injuries.
Surgical Options
Surgery may be recommended in severe cases or when pain persists despite non-surgical treatments. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive option, where the shoulder is repaired through tiny incisions. In some cases, open surgery may be recommended instead.
Total replacement surgery is an option for some conditions. Reverse replacement surgery may become an option if the rotator cuff is severely damaged.
An experienced orthopedic surgeon can evaluate the injury and guide the best treatment options and surgical interventions for your specific case.
Preventing Future Shoulder Pain
Proactive steps, such as maintaining proper posture, engaging in strengthening exercises, and making ergonomic adjustments, can reduce the risk of shoulder problems.
- Proper Posture: Good posture reduces strain on shoulder muscles and joints. Poor shoulder posture can lead to imbalances and increased stress, making the shoulder more susceptible to injuries. Ergonomic adjustments at work or home can help with maintaining proper posture.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporating shoulder strengthening exercises into your routine enhances muscle stability and reduces the risk of injury. Exercises such as shoulder shrugs, arm circles, and resistance training of the shoulder, back and arms can boost muscle strength and joint stability.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Optimizing your workstation setup for comfort can prevent shoulder problems. Consider making adjustments like setting your monitor at eye level to position your arms in a way that reduces shoulder strain. Additionally, using an ergonomic chair to maintain a neutral spine position while sitting can help alleviate stress on the shoulder region.
Summary
Shoulder pain is a common issue that can significantly impact your quality of life. Understanding the common causes, such as rotator cuff tears, bursitis, and arthritis, is the first step toward effective treatment. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical advice can prevent further damage and facilitate quicker recovery.
Effective treatments range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to medications and surgical options. By incorporating preventive strategies such as maintaining proper posture, engaging in strengthening exercises, and making ergonomic adjustments, you can reduce the risk of future shoulder pain and enjoy a healthier, more active life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of shoulder pain?
Shoulder pain is commonly caused by rotator cuff tears, bursitis, and arthritis, which can result in discomfort and restricted movement. Other conditions and injuries can lead to shoulder pain as well.
What are the treatment options for rotator cuff tears?
The treatment options for rotator cuff tears include rest, ice, pain relievers, physical therapy, and corticosteroid injections, while some cases may require surgical intervention to allow for proper healing. It’s essential to consult with a shoulder specialist to determine the best approach for your condition.
How can I prevent future shoulder pain?
To prevent future shoulder pain, focus on maintaining proper posture, engaging in shoulder strengthening exercises, and making ergonomic adjustments in your daily environment. Implementing these strategies will help reduce strain and protect your shoulder health.
When should I see a doctor for shoulder pain?
Consider seeing a doctor for shoulder pain if it persists, interferes with daily activities, or is accompanied by symptoms like sudden swelling or difficulty moving the joint. Early diagnosis is the first step in effective recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Common causes of shoulder pain include rotator cuff tears, bursitis, and arthritis, each with specific symptoms and treatment options.
- Recognizing symptoms is important for timely diagnosis and treatment of shoulder issues.
- Effective shoulder pain management involves rest, physical therapy, medications, and in severe cases, surgical interventions to restore function and alleviate discomfort.
If shoulder pain is disrupting your daily routine, schedule a consultation with one of our experts today.
